Why people fix betting sports
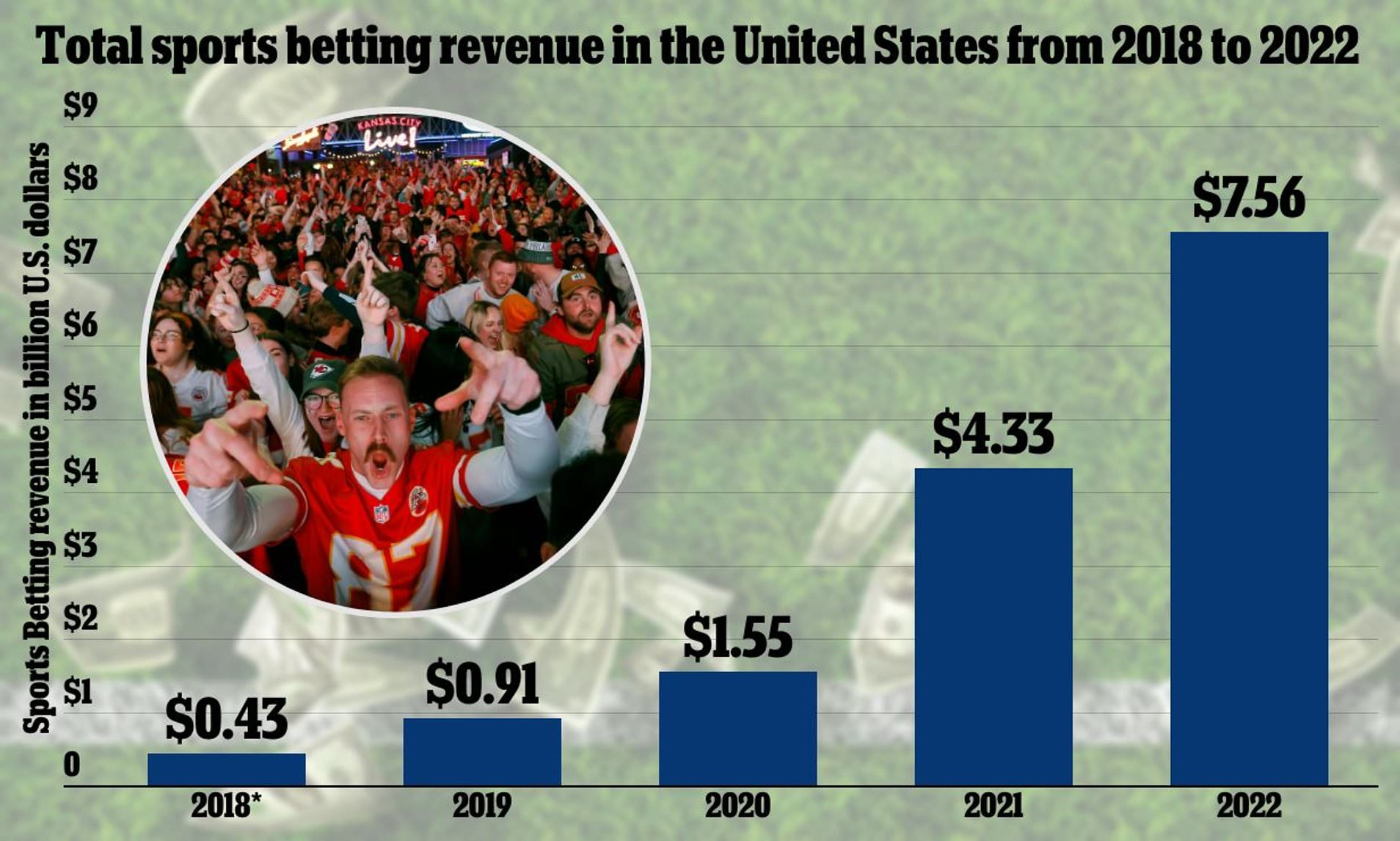
Match fixing is a practice which involves the participants in a sporting event trying to fix the result of the match they are playing in to ensure a. Why people fix betting sports the perspective of illegal operators, “sports betting is not a very profitable business” because the bets are small, there is a risk for. A lack of money in local leagues increases vulnerability to match-fixing attempts. The highly-paid elite player may be able to resist the temptation of a big. People who live closer to casinos are more likely to develop a gambling addiction. Conversely, it's reasonable to assume that if a person lives.
Exploring the Dynamics of Fixing in Sports Betting
Sports have always been a realm where passion meets competition, where the unpredictable nature of events keeps fans at the edge of their seats. However, behind the glitz and glamour of the sports world, a dark shadow looms — the issue of fixing in sports betting. What drives individuals to manipulate outcomes, tarnishing the spirit of fair play and sportsmanship?
Profit Motive: One of the primary reasons behind fixing in sports betting is the lure of financial gain. For some individuals, the prospect of making quick and substantial profits outweighs any moral considerations. Whether it's players, officials, or external entities, the pursuit of money can lead to compromises in integrity.
Deep-rooted Greed: In some cases, the desire for wealth and power can drive individuals to engage in fixing sports events. The insatiable hunger for more money, coupled with a lack of ethical principles, can push people into corrupt practices that undermine the purity of sports.
External Influence: Another influencing factor in the world of sports fixing is external pressure or manipulation. Powerful entities seeking to control outcomes for their benefit can coerce individuals, creating a web of deceit that extends its reach into various levels of sporting events.
Lack of Oversight: Weak governance structures and inadequate regulatory measures within the sports industry can create fertile ground for fixing activities to thrive. Without proper monitoring and enforcement mechanisms in place, perpetrators find loopholes to exploit, perpetuating the cycle of corruption.
Conclusion
The phenomenon of fixing in sports betting is a stain on the reputation of sports worldwide. Whether driven by greed, external pressure, or the pursuit of profit, individuals involved in such practices not only betray the trust of fans but also threaten the essence of fair competition. It is imperative for stakeholders in the sports industry to strengthen oversight measures, enforce strict regulations, and promote a culture of integrity to safeguard the authenticity and credibility of sports.
Betting in UK sport: match fixing
Which sport has most match-fixing? Cricket. Some of the most notorious instances of match fixing have been observed in international cricket. In 2000 the Delhi police intercepted a conversation between a blacklisted bookie and the South African cricket captain Hansie Cronje in which they learnt that Cronje accepted money to throw matches.
Are sports betting fixed? But the general answer is sports betting fixed. I have to say in the vast majority of cases it is not the games are clean.
What is the point of match-fixing? Put simply, match-fixing is dishonest activity to make sure that one team or individual wins a particular sports match. Under the Crimes Act 1961, match-fixing is the manipulation of the overall result of a sports match or racing event (or any event within the match or event) with intent to influence a betting outcome.
Desperate is never a good look. And desperate never makes good money decisions either. Oh, and let's just be clear here—your odds of getting rich off sports betting apps are low. It takes a huge bank roll to actually make money long term.How common is match-fixing in sport? Overall, across all sports, the suspected manipulation rate stood at one in every 476 matches – an increase compared to the manipulation rate of one in every 545 matches in 2021 – demonstrating that even while the vast majority of sporting events are free from betting corruption, the threat of match-fixing is still ...
Why do people think sports betting is bad? The problem with gambling is the subtle way it can take over your behavior and sensibility. This change can happen slowly or quite rapidly depending on a number of variables. However, the outcomes tend to be the same: damage to your relationships, bank accounts, credit rating, and overall mental and physical health.
Do people actually get rich off sports betting? Sports Betting and Your Money
The rise of sports betting could kill off an entire sports league
Such collusion is often not limited to individual games, rather, owners may deliberately try to transfer all of their best players to the more lucrative team. A particularly notorious example occurred in the Major League Baseball season when the owners of the Cleveland Spiders bought a more profitable team, the St. Louis Perfectos , and brazenly traded Cleveland's best players to St.
The Spiders finished the season 20— by far the worst record in MLB history and were contracted after the season. Modern major sports leagues usually prohibit such ownership arrangements. Where it is necessary or desirable for a single ownership group to control two teams, salary caps often limit the ability of owners to stack one roster at the expense of another.
An example of this arrangement occurred in the early 21st century in the Canadian Football League ; between and , the BC Lions and the Toronto Argonauts were owned by the same person. Bookmakers in the early 21st century accept bets on a far wider range of sports-related propositions than ever before. Fixing the result of a more-particular proposition might be seen as less likely to be noticed.
For example, the disgraced former National Basketball Association referee Tim Donaghy has been alleged to have perpetrated some of his fixes by calling games in such a manner as to ensure more points than expected were scored by both teams, thus affecting " over-under " bets on the games whilst also ensuring that Donaghy at least did not look to be outright biased. Also, bets are increasingly being taken on individual performances in team sporting events, which, in turn, has seen the rise of a phenomenon known as spot fixing although it is now unlikely that enough is bet on average players to allow someone to place a substantial wager on them without being noticed.
One such attempt was described by retired footballer Matthew Le Tissier , who in admitted that while he was playing with Southampton FC back in , he tried and failed to kick the ball out of play right after the kick-off of a Premier League match against Wimbledon FC so that a group of associates would collect on a wager made on an early throw-in.
She was free to play normally for the rest of the match. Similarly, in , Pakistani cricket players were accused of committing specific no-ball penalties for the benefit of gamblers. Following investigations by the News of the World and Scotland Yard, on 1 November , Majeed, Pakistan's captain, Salman Butt , Mohammad Asif and Mohammad Amir were found guilty of conspiracy to cheat at gambling and to accept corrupt payments.
Whenever any serious motivation for teams to manipulate results becomes apparent to the general public, there can be a corresponding effect on betting markets as honest gamblers speculate in good faith as to the chance such a fix might be attempted. Some bettors might choose to avoid wagering on such a fixture while others will be motivated to wager on it, or alter the bet they would otherwise place.
Such actions will invariably affect odds and point spreads even if there is no contact whatsoever between teams and the relevant gambling interests. The rise of betting exchanges has allowed such speculation to play out in real time. Evidence of match fixing has been found throughout recorded history, [47] and the history of match fixing is closely related to the history of illegal gambling.
The ancient Olympic Games were almost constantly dealing with allegations of athletes accepting bribes to lose a competition [49] and city-states which often tried to manipulate the outcome with large amounts of money. These activities went on despite the oath each athlete took to protect the integrity of the events and the severe punishment sometimes inflicted on those who were caught.
Chariot racing was also dogged by race fixing throughout its history. By the end of the 19th century gambling was illegal in most jurisdictions, but that did not stop its widespread practice. Why people fix betting sports Boxing soon became rife with fighters "taking a dive", likely due to boxing being a sport involving individual competitors, which makes its matches much easier to fix without getting caught.
Baseball also became plagued by match fixing despite efforts by the National League to stop gambling at its games. Matters finally came to a head in when eight members of the Chicago White Sox threw the World Series. In an effort to restore confidence, Major League Baseball established the office of the Commissioner of Baseball , and one of Kenesaw Mountain Landis 's first acts was to ban all involved players for life.
MLB Rule 21 prohibits players from participating in any form of betting on baseball games, and a lifetime ban for betting on a player's own games. A poster with Rule 21 must be posted on all professional baseball clubhouses. In the s, match fixing in Asia was especially common. It is believed that the word Yaocho came from the name "Chobei" of the owner of a vegetable stand yaoya during the Meiji period.
Created from the first syllable of Yaoya and chobei , the word yaocho was created for a nickname of Chobei. Chobei had a friend called "Isenoumi Godayu" 7th Isenoumi stablemaster with whom he played the game Igo , who had once been a sumo wrestler "Kashiwado Sogoro" former shikona : "Kyonosato" and now was a " toshiyori " a stablemaster of sumo. Although Chobei was a better Igo player than Isenoumi, he sometimes lost games on purpose to please Isenoumi so that Isenoumi would continue to buy merchandise from his shop.
Economists using statistical analysis have shown very strong evidence of bout fixing in sumo wrestling. The sumo association appears to make a distinction between yaocho the payment of money to secure a result and koi-ni-yatta mukiryoku zumo the deliberate performance of underpowered sumo in which an opponent simply lays a match down without exchange of money.
The intricacies of Japanese culture, which include subordination of individual gain to the greater good and knowing how to read a situation without the exchange of words I know my opponent's score, he needs help, and I should automatically give it to him mean that the latter is almost readily accepted in the sumo world and is also nearly impossible to prove.
Some of the most notorious instances of match fixing have been observed in international cricket. In the Delhi police intercepted a conversation between a blacklisted bookie and the South African cricket captain Hansie Cronje in which they learnt that Cronje accepted money to throw matches.  A court of inquiry was set up and Cronje admitted to throwing matches.
A court of inquiry was set up and Cronje admitted to throwing matches.
He was immediately banned from all cricket. Jadeja was banned for 4 years. Although Cronje was a kingpin of betting, following untimely death in most of his fixing partners escaped law enforcement agencies. Earlier in , Australian players Mark Waugh and Shane Warne were fined for revealing information about the 'weather' to a bookmaker.
The fourth Test of Pakistan's summer cricket tour of England contained several incidents of spot fixing , involving members of Pakistan team deliberately bowling no-balls at specific points to facilitate betting through bookmakers. Sreesanth and two other players were banned by the Board of Control for Cricket in India for alleged match fixing.
The investigation was dropped by Sri Lankan authorities and the International Cricket Council in due to a lack of evidence. In July , it was reported that local authorities had shut down an operation in Gujarat , India, that had been running a fictitious, kayfabe version of the Indian Premier League in an attempt to scam Russian sports betters. The matches took place on a field with floodlights , with players dressed in replica jerseys of real IPL teams; based on bets received on a Telegram channel, umpires instructed the players and "referees" to perform specific plays and calls.
Broadcasts of the "matches" were streamed on YouTube , and utilized artificial crowd noise , a sound-alike of cricket commentator Harsha Bhogle , and camera angles that never showed clear shots of the pitch, players, or deliveries. The participating players were paid rupees per-game, and the operation was estimated to have scammed punters out of , rupees before it was shut down by police.
The actual Indian Premier League had already concluded at the end of May. In the European football powerhouse Juventus F. During the subsequent investigation, many top Korean players were also found to be involved in match fixing after the initial discovery. In professional wrestling , most matches have predetermined results; however, as it is an open secret that professional wrestling is staged, it is not considered match fixing.
Up until the s, professional wrestling was considered a legitimate sport. This did not endure as professional wrestling became identified with modern theatrics or admitted fakery , moving away from actual competition. The "worked", known as " kayfabe " nature of wrestling led critics to deem it an illegitimate sport, particularly in comparison to boxing , amateur wrestling , and, more recently, mixed martial arts.
Many individuals began to doubt the legitimacy of wrestling after the retirement of Frank Gotch in Nevertheless, wrestling was still regulated by state athletic commissions in the United States well into the s, until Vince McMahon , owner of the World Wrestling Federation , convinced the state of New Jersey in that wrestling was considered a form of entertainment or " sports entertainment ", as McMahon used rather than as a legitimate sport, and that it should not be regulated by state athletic commissions.
Due to the lingering legitimacy issues that surrounded wrestling from the s until the s, gambling was generally not allowed on wrestling matches while it was still considered a legitimate sport. Despite wrestling having openly acknowledged that the results are predetermined for years, since the late s gambling has increased on wrestling events, though the maximum bets are kept low due to the matches being predetermined.
In the s, the producers of several televised quiz shows in the United States were found to have engaged in match fixing, as part of an effort to boost viewer interest and ratings. At the time, the majority of television programs were effectively controlled by their single sponsors, with broadcasters only providing studios and airtime.
The most infamous example of this strategy came when champion Herbert Stempel was to be replaced by Charles Van Doren —a Columbia University English teacher whom the producers felt would be more popular with viewers. Among them, he incorrectly guessed that On the Waterfront was the winner of the Best Picture award at the 28th Academy Awards.
The correct answer was Marty , which was also one of Stempel's favorite films. The cancellation of the competing quiz Dotto under similar allegations prompted a U. The scandal resulted in regulations being implemented to prohibit the rigging of game shows and other contests by broadcasters. Major scandals have included those of the iBuyPower and NetcodeGuides.
By monitoring the pre-match betting markets it is sometimes possible to detect planned match fixing. It is also possible to detect on-going match manipulation by looking at the in-game betting markets. Several federations have employed services that provide such systems for detecting match manipulation. In addition, several federations run integrity tours where players and officials participate in educational workshops on how match fixing work and how they are prevented.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version. Collusion to secretly predetermine the outcome of a sports match. Is online sports betting legal in wyoming For the album, see Throwing the Game album. This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards.
You can help. The talk page may contain suggestions. September Main article: Match fixing related to gambling. Main article: Tanking sports. Further information: Match-fixing in professional sumo. Main article: Kayfabe. Main article: Quiz show scandals. Washington Post. Archived from the original on 15 May Retrieved 30 July Aldridge, David 5 March Archived from the original on 7 August Gold-Smith, Josh Archived from the original on 12 August Wolff, Alexander 30 August Sports Illustrated.
Wyshynski, Greg 2 March Yahoo Sports. Archived from the original on 29 November Wilson said he was approached by his general manager — at that time, George McPhee — to tank the season. Archived from the original on 30 July Bieler, Des 24 February Archived from the original on 28 September Kelson, Ben 1 August The New York Times.
London, England, United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 9 March Staff and agencies in London 1 August Archived from the original on 28 November Gambling Insider. Archived from the original on 19 April Retrieved 24 January The Fix: Soccer and Organized Crime. ISBN Making the majors: The transformation of team sports in America.
Harvard University Press. Archived from the original on Retrieved Retrieved April 10, The Guardian. Archived from the original on 22 June Retrieved 20 January Archived from the original on December 1, Retrieved December 1, Tampa Bay Times. February 19, Archived from the original on 3 September Retrieved 13 February National Post. Archived from the original on 2 August Archived from the original on 2 April Retrieved 2 April The Daily News Journal.
Murfreesboro, Tennessee. Archived from the original on February 24, Retrieved February 23, Early Lead. Why people fix betting sports The Washington Post. Archived from the original on April 2, Retrieved March 19, Panthers and Patriots face the question". Tanks to '84, the lottery was born". New York: Daily News, L. Archived from the original on July 7, Retrieved August 22, USA Today.
Gannett Co. Archived from the original on January 23, Archived from the original on September 29, Retrieved September 29, The Athletic. Archived from the original on May 29, Retrieved October 7, Archived from the original on January 13, Retrieved December 23, Prizefighting: An American History. Jefferson, N. Retrieved October 30, Inside Bay Area. Archived from the original on October 24, Retrieved October 24, The San Francisco Call.
August 14, Archived from the original on October 31, Retrieved October 31, An indolent Sevilla lets Oviedo win in a shameful match". Mundo Deportivo. San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on February 13, Retrieved November 23, New York Times. Archived from the original on 19 June Retrieved 19 June Feral House. Retrieved 4 September Financial Times.
Archived from the original on 28 August November Archived from the original on 4 November Retrieved 3 November London: The Observer, UK. Archived from the original on 27 September Retrieved 12 December The Telegraph. BBC News. International Journal of the History of Sport. S2CID Match fixing within a specific sport is seen as an issue to be solved internally through appropriate rules and penalties drawn up by the various governing bodies.
These rules, introduced from 1 August , apply to everyone involved in football, from the players and managers, to the match officials and club staff. Participants covered by the ban are prohibited from betting, either directly or indirectly, on any football match or competition that takes place anywhere in the world. The passing of inside information to somebody that uses the information for betting is also prohibited.
One of the fundamental aspects of the sporting competition is maintaining the so-called level playing field. Accordingly, offences of match fixing, which affect this level playing field, are seen as an important a problem as that of doping and illegal drug use in the sporting context. Under the Gambling Act , all bookmakers are required to share information with sporting governing bodies and to alert them to suspicious betting activities surrounding sporting contests.
This condition is viewed as a crucial tool in preventing and detecting betting-related fraud. The Fraud Act adds the offence of fraud to the list of criminal offences contained within the Gambling Act This provision will often be used to prosecute individuals involved in match fixing who are outside the scope of prosecution by the sporting governing bodies.
This would include corrupt groups which run betting syndicates relying on the fixing of matches to make money. Nicola Laver LLB. Nicola is a dual qualified journalist and non-practising solicitor. She is a legal journalist, editor and author with more than 20 years' experience writing about the law. When you submit your details, you'll be in safe hands. They are the UK's leading personal injury service.
Their friendly legal services advisers will call you to talk about your claim and give you free, no-obligation advice. National Accident Law may pay us a marketing fee for our services. By submitting your personal data, you agree for your details to be sent to National Accident Law so they can contact you to discuss your claim.
Your solicitor will discuss any fees before starting your case. Free, no obligation advice from expert UK solicitors. Tens of thousands of people have started their claims with us - you'll be in good company. Decades of experience in personal injury claims.
Popular Pages
- What does cover mean in sports betting
- How to bet on sports in vegas
- Is online sports betting legal in oklahoma
- Is bet on sports app real money
- How do i file taxes for overseas sports betting
- How can i make money on sports bets
- What does it mean to leverage a sports bet
- Can you mystery bet on sports bet
- How to become a professional gambler sport bet
- Where to bet on sports in canada