How is sports betting regulated in the usa

regulation of legal sports betting. 1. Licensing. How is sports betting regulated in the usa U.S. jurisdiction with legal sports betting (referred to hereinafter simply as. “Jurisdictions. Congress has used its power under the Commerce Clause to regulate interstate gambling, international gambling, and relations between the United States and. U.S. Rep. Paul Tonko, a New York Democrat, said his SAFE Bet Act will offer regulation to protect people in the U.S. from gambling-related. Although four states (Nevada, Delaware, Oregon and Montana) had exemptions from the PASPA law and could run retail sports betting way before.
The Regulation of Sports Betting in the USA
Across the vast landscape of American sports, behind the adrenaline-pumping moments and the roaring crowds, lies a complex web of regulations governing the world of sports betting. As a crucial economic and entertainment sector, the United States has been working tirelessly to navigate the legal waters surrounding this form of wagering. Let's delve into the intricacies of how sports betting is regulated in the USA.
The Legal Landscape:
Sports betting regulation in the USA is primarily determined by individual states rather than a federal mandate, following the landmark decision by the Supreme Court in 2018. The ruling in Murphy v. NCAA effectively lifted the federal ban on sports betting, allowing states to legalize and regulate betting within their jurisdictions. Since then, a wave of states has embraced this newfound freedom, with varying approaches and regulations.
State-by-State Variations:
Currently, more than half of all states have legalized sports betting in some form, ranging from full-scale mobile wagering to limited in-person betting at physical locations such as casinos or racetracks. While some states have opted for a free market approach, others have established regulatory bodies to oversee and enforce betting rules.
States like New Jersey and Nevada are considered pioneers in the realm of sports betting regulation, having implemented comprehensive frameworks that prioritize consumer protection, responsible gambling practices, and revenue generation. Through stringent licensing requirements and robust monitoring systems, these states have set a benchmark for others to follow.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the progress made in regulating sports betting, challenges persist on multiple fronts. One significant issue is the lack of uniformity across states, leading to potential inconsistencies in rules and oversight. Additionally, concerns about match-fixing, underage gambling, and addiction loom large, necessitating continued vigilance and proactive measures.
On the flip side, the legalization of sports betting presents a wealth of opportunities for stakeholders. From increased tax revenues for state coffers to job creation and enhanced fan engagement, the benefits are manifold. By striking a balance between regulation and innovation, the USA can harness the full potential of this burgeoning industry.
The Road Ahead:
As the landscape of sports betting continues to evolve, a cohesive and adaptable regulatory framework is essential for ensuring the integrity of sports competitions and the well-being of consumers. Through collaboration between states, industry players, and regulatory bodies, the USA can chart a course that maximizes the benefits of sports betting while mitigating potential risks.
Ultimately, the regulation of sports betting in the USA is a dynamic process that demands ongoing attention and refinement. By staying ahead of the curve and embracing best practices, the nation can foster a thriving sports betting ecosystem that upholds the values of fairness, transparency, and responsible gambling.
Sports Betting Laws by State
Are gambling laws state or federal? In the United States, legal gambling on sports, horse races, and other betting events is regulated by the federal and state governments. People who illegally gamble using “bookies” have been booming for decades. However, the US government is more concerned with illegal gambling businesses, not individuals.
Why is gambling so heavily regulated? GOVERNMENTS SET THE RULES
How does the government regulate gambling? Agents and investigative auditors inspect premises where gambling is conducted; examine gambling equipment; audit papers, books, and records of the gambling establishment; investigate suspected violations of gambling laws; coordinate multijurisdictional investigations; investigate complaints lodged against licensees by ...
Is sports betting federally regulated? In 2018, the Supreme Court overturned the federal ban on sports betting, allowing state governments to set their own policies on the matter. 5 Although it is now possible for sportsbooks to operate legally in the U.S., no legislation has been passed on a federal level legalizing the activity.
Thus, to the extent that governments assume a general responsibility to shield their populations from fraud, regulation is the most effective means of ensuring that such legal gambling as does exist is fair and honest. A second area of government concern is crime, especially organized crime.How is online gambling regulated in the United States? Online gaming is regulated by three main federal laws: the Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act (UIGEA), The Wire Act, and the Indian Gaming Regulatory Act (IGRA). The Federal Wire Act is one of the older federal statutes, while the UIGEA is a recent law that regulates financial transactions.
Who regulates gambling USA? Each state determines what kind of gambling it allows within its borders, where the gambling can be located, and who may gamble. Each state has enacted different laws pertaining to these topics.
When did sports gambling become federally legal? Sports betting became possible in May 2018 when the Supreme Court struck down the Amateur Sports Protection Act. Since then, 38 states as well as the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico have legalized some form of sports betting though not all have implemented it.
How many states have legislation regulating gambling? Sports gambling is legal in 38 states.
First Came the Sports Betting Boom. Now Comes the Backlash.
All other states that allow casino-style gambling restrict it to small geographic areas e. As domestic dependent nations, American Indian tribes have used legal protection to open casinos, which has been a contentious political issue in California and other states. In some states, casinos are restricted to " riverboats ", large multi-story barges that are permanently moored in a body of water.
Online gambling has been more strictly regulated: the Federal Wire Act of outlawed interstate wagering on sports, but did not address other forms of gambling; it has been the subject of court cases. The Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act of UIGEA did not specifically prohibit online gambling; instead, it outlawed financial transactions involving online gambling service providers—some offshore gambling providers reacted by shutting down their services for US customers.
On July 1, , a new law took effect in the state of South Carolina , whereby the ownership, possession, or operation of a video poker machine, for either commercial or personal use, became illegal. Violators are subject to prosecution and substantial fines. Through at least , the only type of legalized gambling in that state is the South Carolina Education Lottery.
Commercial casinos are founded and run by private or public companies on non-Native American land. There are 24 states and three U. The history of native American commercial gambling began in , when the Seminoles began running bingo games. Native Americans were familiar with the concept of small-scale gambling, such as placing bets on sporting contests. For example, the Iroquois, Ojibways, and Menominees would place bets on games of snow snake.
By , about three hundred native American groups hosted some sort of gaming. Some native American tribes operate casinos on tribal land to provide employment and revenue for their government and their tribe members. Tribal gaming is regulated on the tribal, state, and federal level.
Native American tribes are required to use gambling revenue to provide for governmental operations, economic development, and the welfare of their members. Federal regulation of native American gaming was established under the Indian Gaming Regulatory Act of Under the provisions of that law, games are divided into three distinct categories:.
Of the federally recognized tribes in , participated in class II or class III gaming by Approximately forty percent of the federally recognized tribes operate gaming establishments. Like other Americans, many indigenous Americans have dissension over the issue of casino gambling. Some tribes are too isolated geographically to make a casino successful, while some do not want non-native Americans on their land.
Though casino gambling is controversial, it has proven economically successful for most tribes, and the impact of American Indian gambling has proven to be far-reaching. How is sports betting regulated in the usa Gaming creates many jobs, not only for native Americans, but also for non-native Americans, and in this way can positively affect relations with the non-native American community.
On some reservations, the number of non-native American workers is larger than the number of Native American workers because of the scale of the casino resorts. Although casinos have proven successful for both the tribes and the surrounding regions, state residents may oppose construction of native American casinos, especially if they have competing projects. The project's objective was to create jobs for the tribes' young people.
The same day the state voted against the Indian casino project, Maine voters approved a plan to add slot machines to the state's harness racing tracks. Class III gaming is under the jurisdiction of the states. For instance, in order for a tribe to build and operate a casino, the tribe must work and negotiate with the state in which it is located. These Tribal-State compacts determine how much revenue the states will obtain from the Indian casinos.
The Indian Gaming Regulatory Act requires that gaming revenues be used only for governmental or charitable purposes. Revenues have been used to build houses, schools, and roads; to fund health care and education; and to support community and economic development initiatives. Indian gaming is the first and essentially the only economic development tool available on Indian reservations.
The classic lottery is a drawing in which each contestant buys a combination of numbers. Plays are usually non-exclusive, meaning that two or more ticket holders may buy the same combination. The lottery organization then draws the winning combination of numbers, usually from 1 to 50, using a randomized, automatic ball tumbler machine.
To win, contestants match their combinations of numbers with the drawn combination. 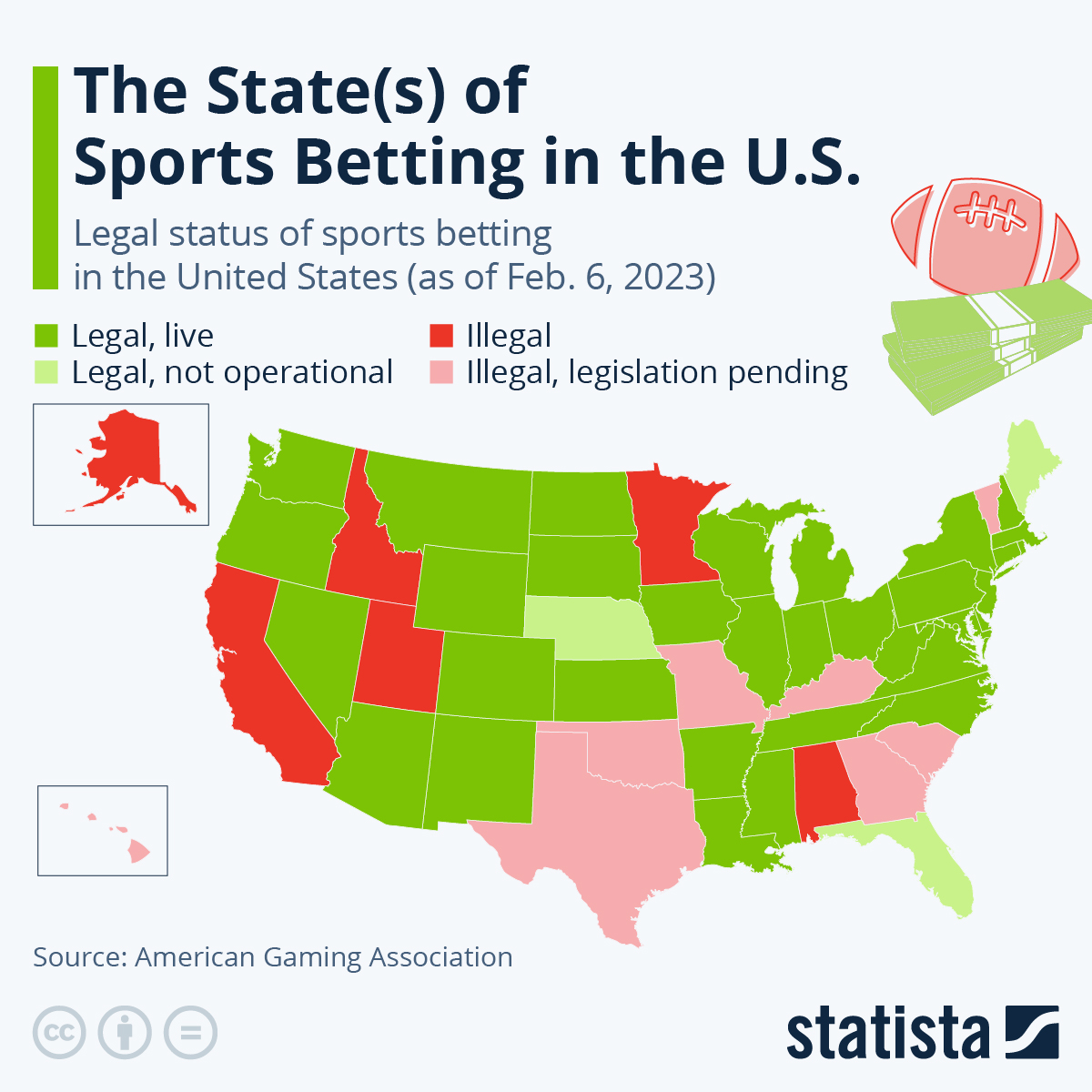 The combination may be in any order, except in some "mega ball" lotteries, where the "mega" number for the combination must match the ball designated as the "mega ball" in the winning combination. If there are multiple winners, they split the winnings, also known as the "Jackpot".
The combination may be in any order, except in some "mega ball" lotteries, where the "mega" number for the combination must match the ball designated as the "mega ball" in the winning combination. If there are multiple winners, they split the winnings, also known as the "Jackpot".
Winnings are currently subject to federal income taxes as ordinary income. Winnings can be awarded as a yearly annuity or as a lump sum , depending on lottery rules. Most states have state-sponsored and multi-state lotteries. There are only five states that do not sell lottery tickets: Alabama, Alaska, Hawaii, Nevada, and Utah.
In some states, revenues from lotteries are designated for a specific budgetary purpose, such as education. Other states put lottery revenue into the general fund. Multi-jurisdictional lotteries generally have larger jackpots due to the greater number of tickets sold. The Mega Millions and Powerball games are the biggest of such lotteries in terms of numbers of participating states.
Some state lotteries run games other than the lotteries. Usually, these are in the scratchcard format, although some states use pull-tab games. In either format, cards are sold that have opaque areas. In some games, all of the opaque material is removed to see if the contestant has won, and how much.
In other scratchcard games, a contestant must pick which parts of a card to scratch, to match amounts or play another form of game. In , the U. It mandated states not to legalize sports betting apart from parimutuel horse racing , dog racing and jai alai. The sports lotteries conducted in Oregon , Delaware , and Montana were exempt, as well as the licensed sports pools in Nevada. As of September , sportsbooks are legal in 37 states the District of Columbia, and the territory of Puerto Rico,with legal sports betting operation also expected to begin in North Carolina later in , Online sports betting also legal in 30 states, Washington D.
According to the Center for Gaming Research University Libraries, legal gambling revenues for were as follows: [1]. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources.
Age requirements also vary, with some states requiring gamblers to be at least 18 years old, while others have a higher minimum age of 21 years old. New York is the only state that has two different age requirements: Gamblers must be at least 21 years old to use commercial casinos and online sportsbooks, while those utilizing tribal casinos only need to be 18 years old.
In , the Supreme Court overturned the federal ban on sports betting, allowing state governments to set their own policies on the matter. Although it is now possible for sportsbooks to operate legally in the U. If you're considering betting money on the outcome of a sporting event, it's important to be aware of the opportunities and restrictions in your state.
Even where sports betting is legal, the odds are stacked against you and there's a much greater risk compared to other ways you could be putting your money to work, such as investing. How to bet on sports online in michigan As such, always make sure you're wagering money that you're certain you can afford to lose. If you or someone you know has a gambling problem, call the National Problem Gambling Helpline at , or visit ncpgambling.
Supreme Court of the United States. National Collegiate Athletic Assn. American Gaming Association. National Council on Problem Gambling. Table of Contents Expand. Table of Contents. Understanding Sports Betting. Sports Betting Laws by State. The Bottom Line. Wealth Lifestyle Advice. Trending Videos.
Key Takeaways Gambling on sporting activities typically requires working with an individual or company that accepts bets, also known as a sportsbook. These can either be retail locations that offer in-person bet placement or online and mobile platforms, depending on state laws. According to the American Gaming Association, 38 states and the District of Columbia have legalized sports betting, meaning single-game sports betting may be offered to consumers through legal retail or online and mobile sportsbooks.
Even when sports betting has been legalized in a state, restrictions may still apply. Corruption in tennis has been long considered as issue. In and , Koellerer was banned for six months due to his bad behavior. In addition, in August , he facilitated betting by placing odds for matches and had links for placing bets. Machine learning models can make predictions in real time based on data from numerous disparate sources, such as player performance, weather, fan sentiment, etc.
Some models have shown accuracy slightly higher than domain experts. Media related to Sports betting at Wikimedia Commons. Contents move to sidebar hide. How is sports betting regulated in the usa Article Talk. Read View source View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Form of gambling. This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page.
Learn how and when to remove these template messages. The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this article , discuss the issue on the talk page , or create a new article , as appropriate. June Learn how and when to remove this template message. This article may be too technical for most readers to understand.
Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts , without removing the technical details. July Learn how and when to remove this template message. This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. See also: Glossary of bets offered by UK bookmakers.
Main article: Bookmaker. This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. September The examples and perspective in this section deal primarily with United States and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this section , discuss the issue on the talk page , or create a new section, as appropriate.
September Learn how and when to remove this template message. Sports betting legal. Sports betting illegal. Arbitrage betting Betting pool Financial betting Friendly political wager Parimutuel betting Point shaving Sports betting systems Statistical association football predictions Virtual sports.
Forbes Betting. Retrieved May 2, Retrieved November 14, International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. Archived from the original PDF on July 23, Journal of Prediction Markets. Retrieved January 11, Retrieved May 9, Chris Christie: "Let them try to stop us" from sports betting". Associated Press. May 25, May 14, A Guide To All 50 States".
Retrieved January 20, October 29, November 6, Retrieved February 22, The New York Times. ISSN October 26, Retrieved November 29, MLB Advanced Media. April 6, Retrieved April 22, March 30, July 19, Supreme Court". March 15, Retrieved October 2, A quick recap of Oliver Luck on radio row. Retrieved February 6, Las Vegas Sun.
June 12, Legal Sports Report. February 8,
Popular Pages
- How can i check my sport bet ticket
- Should betting on sports be legal pdf
- Is sports betting legal in utah
- How to place a sports bet at meadowlands
- How to bet on sports legally
- How to make 100k sports betting
- What is a banker in sports betting
- What is the best online sports betting site
- Does bovada allow parlay bets on sports
- How to build a sports betting model in python