Can us citizens bet on sports online
Legal sports betting launched in Colorado in May,and their law stipulates that online sportsbooks must partner with a local casino in order to legally. 38 states and Washington, D.C. have legalized sports betting since the federal ban on sports gambling was struck down in Gone are the days. Can I sign up for the DraftKings Sportsbook even if I'm not a resident of a state that allows sports betting? (US). Yes, absolutely! Online can us citizens bet on sports online betting is now legal in 29 states and in D.C. Professional and casual bettors alike can turn to their smartphones to download an.
The Legal Landscape of Online Sports Betting for US Citizens
In recent years, the debate surrounding online sports betting in the United States has gained significant traction, with many citizens eager to engage in this popular form of entertainment. However, the legal landscape surrounding online sports betting in the US is complex and varies from state to state.
State Regulations and Variation
As of now, online sports betting is legal in several states across the country, including New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Nevada, and more. Each state has its own set of regulations and requirements that operators must adhere to, creating a patchwork of rules that can be challenging to navigate for both consumers and providers.
Federal Law Implications
While some states have embraced online sports betting, it's essential to understand that there are still federal laws in place that restrict or prohibit certain forms of online gambling. The Federal Wire Act, for example, prohibits the use of interstate wires for sports betting, which has implications for online platforms that operate across state lines.
Offshore Betting Sites
For US citizens looking to engage in online sports betting, offshore betting sites present a tempting but risky option. While these sites may offer a wider range of betting options and more competitive odds, they operate outside of US laws and regulations, leaving consumers vulnerable to potential risks and legal complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the landscape of online sports betting for US citizens is a complex and evolving one, with a mix of state and federal regulations shaping the industry. While some states have embraced online sports betting, others are still navigating the complexities of legalization. As a result, individuals interested in betting on sports online should educate themselves on the laws and regulations in their state to ensure they are engaging in lawful and safe practices.
Where Is Sports Betting Legal? Projections for All 50 States
How do you bet on sports USA? Most sportsbooks make it quite easy.
- Navigate to your desired game and bet type.
- Click the "bet cell"
- The bet will populate in your bet slip.
- Enter your bet amount.
- Submit bet.
Is bet on sports app legit in USA? The Bet On Sports App mobile application for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches and other mobile devices is for entertainment purposes only, and is not a gambling operator.
How do I bet on bet365 in USA? How to use bet365 on your Windows and Mac computer
- Download a VPN onto your computer. Our top recommendation is NordVPN.
- Install the VPN and connect to a server in a location that gets full access to bet365 – like the UK.
- Head to the bet365 website, create an account, or sign in.
- Now you can bet on your favorite sports!
Where is BetOnline legal? Online sports betting is not yet legal in California. Online sports betting is live and legal in Colorado. Online sports betting is live and legal in Connecticut. Online sports betting is live and legal in Delaware.
Can Americans bet on bet365? As of the latest update, bet365 offers legal online betting to US players who are 21 years old and over, with an exception in Kentucky where individuals 18 and older can participate.
Is it allowed to operate an online gambling site in US? The Department of Justice maintains that, under the Wire Act, all Internet gambling by bettors in the United States is illegal.
Sports Betting Laws by State
Presumably, the age 21 restriction is due to the sale of alcohol in that location. A standard strategy for avoiding laws that prohibit, constrain, or aggressively tax gambling is to locate the activity just outside the jurisdiction that enforces them, in a more "gambling friendly" legal environment. Gambling establishments often exist near state borders and on ships that cruise outside territorial waters.
Gambling activity has also exploded in recent years in Native American territory. Internet-based gambling takes this strategy and extends it to a new level of penetration, for it threatens to bring gambling directly into homes and businesses in localities where a physical gambling establishment could not conduct the same activity. In the s, when the World Wide Web was growing rapidly in popularity, online gambling appeared to represent an end-run around government control and prohibition.
A site operator needed only to establish the business in a friendly offshore jurisdiction such as the Bahamas and begin taking bets. Anyone with access to a web browser could find the site and place wagers by credit card. Confronted with this blatant challenge to American policies, the Department of Justice and Congress explored the applicability of current law and the desirability of new regulation for online gambling.
In exploring whether an offshore Internet gambling business taking bets from Americans violated federal law, attention was focused on the Wire Act, 18 U. The operator of a wagering business is at risk of being fined and imprisoned under the Wire Act if the operator knowingly uses a "wire communication facility" to transmit information related to wagering on "any sporting event or contest.
An exception exists if that act is legal in both the source and destination locations of the transmission. Attorney E. The Fifth Circuit disagreed, ruling that the Wire Act applies only to sports betting, not other types of gambling. In , Congress passed the Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act , which made it illegal for wagering businesses to knowingly accept payment in connection with unlawful Internet gambling though it does not itself make Internet gambling illegal.
It also authorizes the Federal Reserve System to create regulations that prohibit financial transaction providers banks, credit card companies, etc. See 31 U. This Act, along with threats of prosecution under the Wire Act from the Department of Justice, has caused several Internet gambling businesses to withdraw from the U. In response, House Representatives introduced multiple bills in to soften federal Internet gambling law.
If passed, the Internet Gambling Regulation and Enforcement Act and the Internet Gambling Regulation and Tax Enforcement Act would license, regulate, and tax Internet gambling businesses rather than prohibit them from taking bets from the United States. Alternatively, the Skill Game Protection Act would clarify the Wire Act to exempt certain games such as poker and chess.
In addition to federal measures, some states have enacted legislation to prohibit some types of Internet gambling. Can us citizens bet on sports online In , Washington State amended its Code to make knowingly transmitting or receiving gambling information over the Internet a felony. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.
Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology. This survey includes a total sample size of Asian adults. The sample primarily includes English-speaking Asian Americans and, therefore, may not be representative of the overall Asian adult population. Despite this limitation, it is important to report the views of Asian Americans on the topics in this study.
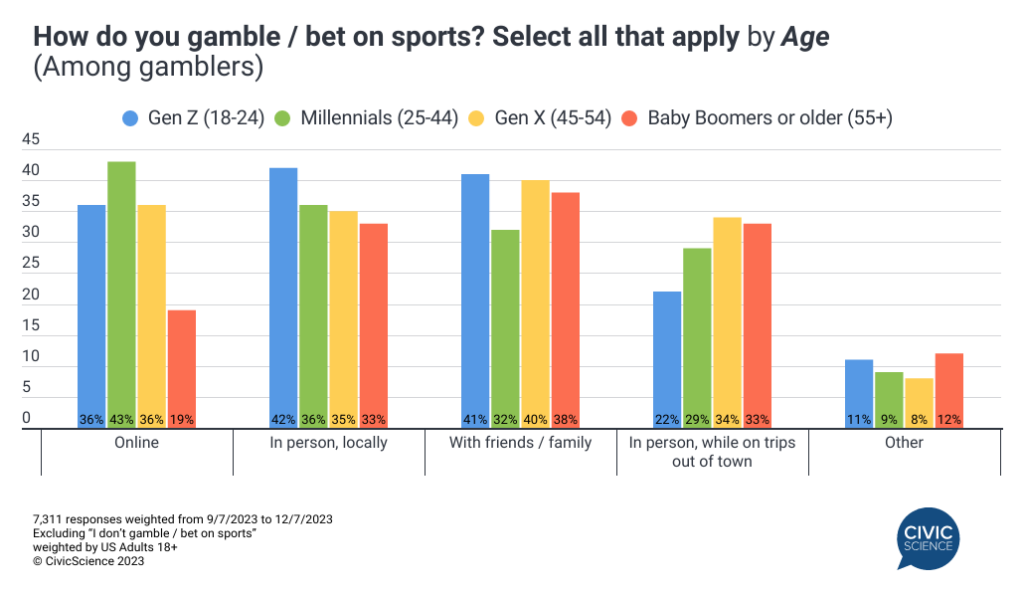
There are no significant differences in self-reported sports betting by educational attainment or household income level. Awareness of legalized sports betting varies by demographic group. Americans ages 50 and older, those with a college degree and those in upper-income households are also among the groups who are more likely to have read or heard about it.
Perhaps not surprisingly, Americans who have read or heard a lot about the widespread legalization of sports betting in the U. The widespread legalization of sports betting has created a new revenue stream for many state governments , but it has also raised concerns about gambling addiction and other societal harms.
So how do Americans feel about the fact that sports betting is now legal in much of the U. The public is slightly more divided on a separate question about whether the widespread legalization of sports betting is a good or bad thing for sports. On these questions, too, there are some demographic differences. 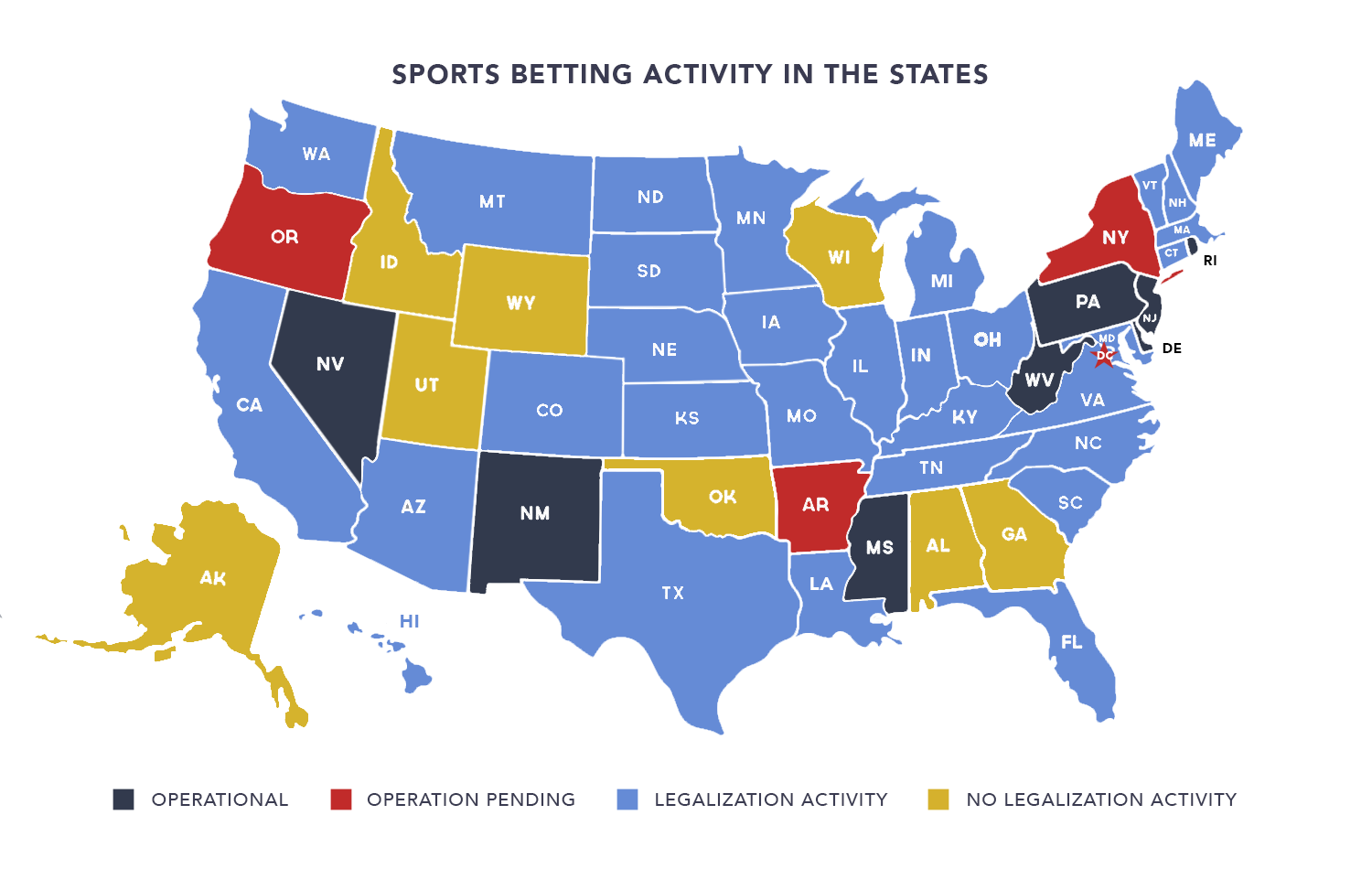 College graduates and those in upper-income households are also more likely to see the widespread legalization of sports betting as a bad thing for both society and sports.
College graduates and those in upper-income households are also more likely to see the widespread legalization of sports betting as a bad thing for both society and sports.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology. About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions.
Popular Pages
- How to start a sports betting business
- Does new mexico have sports betting
- How do sports betting decimals work
- Can nfl players bet on sports
- Do guys actually make a living betting on sports
- Does rivers casino have sports betting
- Are any sporting bets tied in with the lott
- Is sports betting lucrative
- What does tot mean in sports betting
- When did online sport betting apps get intoduced